How E-Invoice Will Impact Business

How E-Invoice Will Impact Business
What Is E-Invoice
e-Invoice is a system to report B2B (Business to business) invoices to the GST system automatically for ease of filing monthly returns. Under the present system, invoices generated by different accounting software used by different businesses are unable to be read by different software systems, nor the GST Network, which requires them to be again manually translated by data entry into the new software. The e-Invoice System is a unified standard that is being introduced so that all the invoices of GST registered invoices can be formatted according to the same standard throughout the whole industry and applicable to all software and platforms automatically.
The following types of documents will need to be e-Invoiced and reported to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) – credit notes by the supplier, supplier invoices, supplier debit notes, any other document required to be disclosed under law.
The e-Invoice proposal was also kept open to public access also for an extended period of time so that members of the business community and other stakeholders may be able to comment and suggest reforms.
Workflow
The workflow of invoice generation can be divided into two steps –
a) Interaction between supplier/seller with IRP & GST/E-Way Bill System
b) Interaction between buyer with IRP & GST/E-Way Bill System
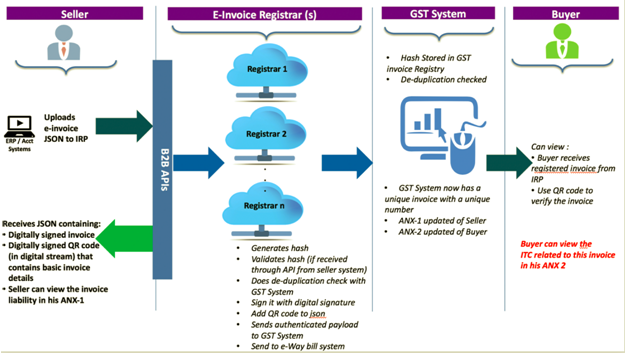
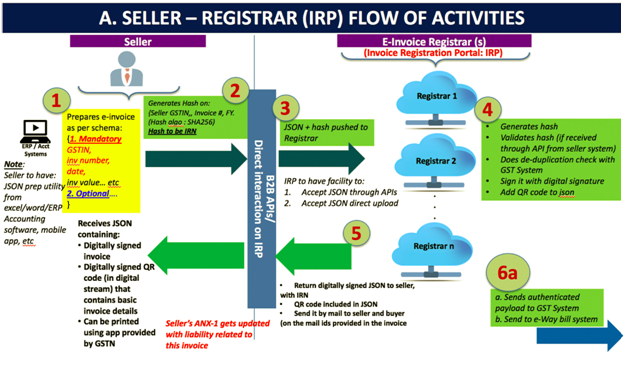
Part A: Flow from Supplier/Seller to IRP
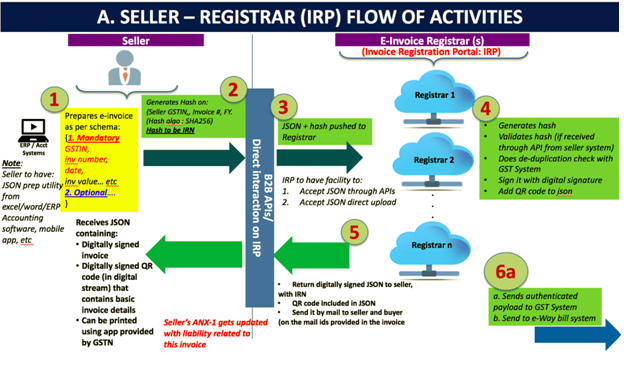
- Step 1 – The invoice is generated by the Seller’s billing or accounting software. This may be a proprietary or third party software compliant with the GST e-Invoice standards Schema or those using EXCEL or GSTN’s provided utility program. It must have the mandatory parameters/fields req. By GST Council guidelines, if not the optional ones. And most importantly, the seller’s software must have the capability to generate a JSON of the final invoice to be upload to the IRP. JSON is a text format in which data travels between servers. This text format can later be re-converted into JAVA Script Objects. Only the JSON gets uploaded not the whole invoice.
- Step 2 – An optional Step in which the Invoice Reference Number (IRN) is generated (in technical terms hash of 3 parameters using a standard and well-known hash generation algorithm e.g. SHA256). Three parameters are required to generate IRN – Supplier GST Identification Number, supplier invoice number and the financial year.
- Step 3 – The JSON of the invoice along with the IRN (if generated) is uploaded into the IRP by the seller. This can be done directly on the IRP or through third-party apps developed by GSPs (GST Suvidha Provider).
- Step 4 – The IRP will validate the hash on the uploaded JSON, and check the hash from the Central Registry on the Central Registry to ensure that the same is invoice is not repeated in the system. A signature is added on the Invoice Data and a QR code is added to the JSON by the IRP. This will contain the seller’s and buyer’s GSTN number, Invoice number and date, number of line items, HSN of major commodity categorized by hash, value, etc. This hash given by the IRP will become the final IRN (Invoice Reference Number) for the e-Invoice which is unique to each invoice. The uniqueness is maintained by keeping a record of invoice hashes in a central registry.
- Step 5 – The uploaded data will be shared in the backend to the server maintained by the GSTN.
- Step 6 – A digitally signed JSON with IRN is given back to the seller along with the QE Code. The registered invoice is also e-mailed to both the buyer and the seller.
Part B: Flow from IRP to GST System/E-Way System & Buyer
- Step 1 – The JSON of the uploaded e-Invoice along with the IRN is shared with the GST system and the E-Way Bill System.
- Step 2 – Update of the ANX – 1 and ANX 2 with the buyer automatically by the GST System to determine liability and the amount of input tax credit.
- Step 3 – E-Way bill system will create Part-A of E-Way bill using this data to which only vehicle number will have to be attached in Part-B of the e-way bill.
Modes of Creation of e-Invoice
The Govt. has made multiple modes available to the taxpayer such as through the Web Portal, using API, SMS, Mobile App, Offline, GST Svidha Provider Third-party software-based – to choose the most convenient way to down the e-Invoice. All services will be provided through the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). API mode would be especially useful for big taxpayers and accounting software providers, as this mode can be used for bulk purposes, where users can queue requests one request after the other, which will be processed by the IRN at less than a fraction of a second each. Printing a hardcopy of the invoice by the customer will look no different than the legacy format, as the e-Invoice system only after the backend schema and not the front end look. An offline app is also provided on the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) to download and authenticate the QR code of the invoice offline. However, only basic details would available and the facility to download the complete invoice is provided to tax officers as under the current E-Way bill system. It is important to note than QR Code verification is offered from the GST System and not the IRP because IRPs do not have the permission to store invoices for more than 1 day. Multiple IRPs will be established to ensure smooth 24/7 operations. The National Informatics Centre (NIC) will be the first Registrar IRP.
Why Was E-Invoice Brought Into The Picture?
Generally, the invoices and raw data generated by one accounting software are not readable by another. They may look the same or similar to human eyes, but to machines, invoices generated by another software is completed un-understandable. For example, an Invoice generated by the SAP system cannot be read by a machine that is using the ‘Tally’ system. This requires additional data entry at every stage when the information is accessed by a new party their own types of accounting or auditing software – as is the current norm. This additional data entry is not only expensive and slow but prone to human errors as well. Similarly, when these invoices generated by a hundred different third party accounting systems interact with the GST system they cannot be automatically understood by the machine without human input. Thus there was a need to build a uniform system of invoicing – the e-Invoicing System which would be capable of being understood by all accounting and the GST systems also.
The introduction of a standard e-invoicing system is extremely crucial to facilitate the ease and speed of doing business. The development of Cross-platform machine readability is thus the objective. A central standard is not only useful for GST Returns filing, but may be utilized by private parties also such as Banks and Auditors to make a quick assessment of the Company, without the need for human data entry fraught with manual errors.
One of the most prominent advantages of the e-Invoice system is that taxpayer businesses will not need to change to a new system. They can keep using their old Accounting programs or ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software. The change required by e-Invoice is only on a backend level. Their previous invoices would look absolutely the same. The GST Schema is attached on the backend to bring the metadata formatting underneath the software into the same standard as in harmony with the GSTN. So that only the JSON data which is transmitted to the GST System is formatted uniformly, nothing else.
Benefits Of E-Invoice System For Businesses
There are many benefits to implementing e-Invoice into the GST System –
Better Services for the Taxpayer
E-Invoices will automate the process of the generation of invoices for GST. This will significantly speed up the process, decrease cost, eliminate human error due to the requirement of manual data entry at every step.
- Elimination of multiple formats by automation of reporting of B2B invoice data (purchase, sale, etc.) in a unified and native format that it is generated in.No need for different formats for the generation of GSTR 1 and e-way bill.
- Sales and Purchase register data (ANX 1 and ANX 2) is automatically generated from this data to keep the Return (RET 1) is pre-prepared and kept ready for filling. This data can be also used to generate an e-Way Bill.
Enhancement of business Process
The format will become a part of the business process and practice of the company. For businesses that are already using accounting software, a unified system format across the industry will help the relationship between businesses and banks, auditors and investors, who can now access the data without first needing to convert it into the format that they are using. For small businesses, who do not use computerized accounting software, the GST Council courtesy of the Govt. is providing free ERP and Accounting software to GST registered business, to boost the Digital India Initiative.
Reduction in Input Tax Verification Issues
Input Tax is the amount of tax already paid for the raw materials in the product (input) which has to be deducted from the taxable amount for the output product. Manual calculations in GST Returns filing often results in mistakes regarding under or over-claiming of input tax credits. This is the amount of deduction a business is entitled to for tax already paid on the product. Inadequate claiming of Input Tax Credit can lead to a substantial loss for the business as well as additional cost and hassle to fix errors. An automated system will eliminate human errors and ensure correct Input Tax information is being entered always.
Ease of Verification of Info before final submission
After submitting the info to the GST System, the system will generate a drat return which can be verified against the actual business invoices to ensure that the correct data is provided. If not the buyer can reject it and start a new process. If accepted the buyer and confirm and the system will generate a final return.
Administrative Efficiency
A lot of fake invoices used to be generated before the e-Invoice system which will now get check as the system becomes automated.
Timeline And Impact On Business Based On Turnover
The e-Invoice system is panned to be rolled out from January 2020 on a voluntary basis. The compulsory nature of the program will be imposed slowly in phases to get the whole system acclimatized to the new software level changes to their accounting standards and business practices. Initially, the scheme will be made compulsory for business over a specific turnover, voluntary for everyone else. After that gradually it will be compulsory universally. It is important to remember that the small and medium-sized taxpayers (having annual turnover below Rs 1.5 Crores) can avail accounting and billing systems being offered by GSTN free of cost.
What Are The Standards Of E-Invoice?
There was a lack of a standard invoicing system in the market and the GST Council with this of e-invoicing has introduced a new standard in consultation with the ICAI (The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India), the Statutory Body regulating the practice and profession of Chartered Accountants in India. The Standard is modelled on the Pan European Public Procurement Online (PEPPOL) which is based on the Universal Business Language Standard (UBL). This standard has been chosen as it takes into account the requirements under statutory tax laws and is in compliance with international business practices as well. The standard also allows for the generation of multiple fields of data not required to be reported under the GST regime. Businesses are free not to generate and report such kind of data if the chose, or are not producing such.
The data generated by an e-Invoice would contain the following parts
- e-Invoice schema: This the technical part which contains, the program interface, API, and the primary rules such as whether a field is mandatory under the GST or not, sample values of fields, etc.
- Masters: Masters are programs which correctly identify and input data into the relevant fields as decided by the GSTN. Fields include, supply type, invoice type, UQC, State Code, etc.
- Template: The template helps the user to relate different terms used and generated in other systems. Mandatory fields are marked in green and optional ones in yellow.
The Standard invoice format is the same for all business types and sizes. This one invoice format will contain all the permitted fields in one file. There are some mandatory. Others are applicable to different sizes and types of business and would be filed by them respectively as applicable and not by the others.






