Common Questions About Life Insurance In India

Common Questions About Life Insurance In India
Table of Contents
1. Why should you invest in a life insurance plan?
- Financial Security
- Accidents and Illnesses
- Investment Options
- Debt Repayment and Collateral
- Tax Benefits
2. What are some typical terms associated with Life Insurance Plans
- Term
- Grace Period
- Free-look Period
- Lapsed Policy
- Sum Assured
- Death Benefit
- Accidental Benefit
- Cash Value
- Reinstatement
- Rider
- Vesting Age
- Waiver of Premium
3. What are the Types of Life Insurance Plans in India?
- TERM INSURANCE PLAN
Types of Term Insurance available in India
Level Term Insurance
Increasing Term Insurance
Decreasing Term Insurance
Term Insurance with Return of Premium (TROP)
- UNIT LINKED INSURANCE PLAN
Types of ULIPs
Equity funds
Debt funds
Type 1 ULIP
Type II ULIP
- ENDOWMENT PLAN
Types of Endowment Plans in India
Unit Linked Endowment Plan
With- Profit Endowment Plan
Full Endowment Plan
Low Cost Endowment Plan
- MONEY BACK INSURANCE PLAN
- WHOLE LIFE INSURANCE PLANS
Types of whole life plans available in India
Non-participating Whole Life insurance Plan
Participating Whole Life Insurance Plan
Level Premium Whole Life Insurance Plan
Limited Payment Whole Life Insurance Plan
Single Premium Whole Life Insurance Plan
Intermediate Premium Whole Life Insurance Plan
- CHILD INSURANCE PLANS
Types of Child Insurance Plans
Unit Linked Child Insurance Plans (ULIP)
Traditional Endowment Plans
What is Vesting Age in Child Insurance Plans?
- PENSION PLANS
Types of Pension Plans in India
Deferred Annuity Plan
Immediate Annuity Plan
With or without cover Pension Plan
National Pension Scheme (NPS)
4. What are the common exclusions in Insurance policies in India?
- Death due to Suicide
- Death as a direct result of the actions of the policy-holder
- Death due to intoxicants or narcotics
- Death due to war or terrorism or natural calamities
- Death due to self-inflicted injury
- Death due to sexually transmitted diseases
5. What are Riders and how can they enhance Insurance Policies?
- Permanent & Partial Disability
- Critical Illness
- Accidental Death
- Waiver of Premium
- Income Benefit
6. Is it a good Idea to buy two or more Life Insurance Plans?
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
7. How to get Tax Benefits on Life Insurance Policies
- Deduction for Premium under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act
- Exemption for Maturity Benefit under Section 10(10D) of the Income Tax Act
8. What are the Factors which affect how much premium is chargeable
- Age
- Health Records and Medical History
- Gender
- Smoking and Drinking
- Profession
- Lifestyle and Hobbies
- Obesity
9. How to decide how much life insurance is needed 18
10. How to File a Life Insurance Claim in case of death of the Insured
11. How to File a complaint against an Insurance Provider?
Life insurance is used to provide enhanced financial security for family members and dependents when they are no longer there, or as security against uncertainty and challenging times. Depending on the specific plans, they can also be used for myriad purposes such as planned expenses like mortgage, vacations and expensive college tuitions through-out the life of the assured.
1. Why should you invest in a life insurance plan?
India has a current population of over 1 billion 369 million people. However, it is estimated more than 988 million Indians, i.e. over 74% of the population doesn’t have a life insurance policy of any kind. Out of the 26% of people who have some life insurance, most of them are only insured for an average of a mere 7.8% of what they would actually need to cover the financial shock of the death of the insured. Here are five of the main reasons why you definitely need to purchase some form of life insurance.
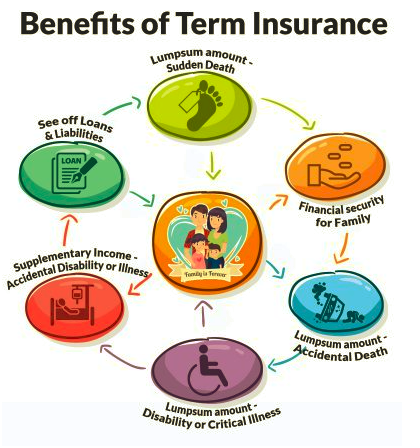
- Financial Security
The most basic objective of life insurance is to provide financial security for your family in case of your death as the primary breadwinner. Life insurance helps to provide for basic daily expenses, riders may ensure milestone expenses like education and ensure that the standard of living for your family doesn’t fall too drastically. This provides you with peace of mind to live your life, known that if something happens to you, your loved ones will be taken care of. - Accidents and Illnesses
The uncertainty of life sometimes puts you in an unfortunate circumstance where you might be injured and seriously disabled by an accident leaving you unable to provide for your family. Riders in life insurance policies take care of hospitalizations and provide periodic payments to substitute your income. - Investment Options
Life insurance plans are used not only for the death benefit, but offer very handsome investment returns also. Policies like ULIPs and endowment policies use your money to invest in the market and provide returns, and these plans can be purchased with an investment objective in mind for extra income or major expenses and luxuries like the purchase of a car or vacations. - Debt Repayment and Collateral
The death benefit from life insurance can be used by your family members to pay off major loans availed during your lifetime. Some plans even provide for payment of periodic bonuses during the term of the policy itself. Thus, in effect, they are used as investment instruments to take care of major expenses like mortgages, real estate, and education. Some plans like whole life policies are also readily accepted as collateral for bank loans.
5. Tax Benefits
Several life insurance policies offer attractive tax saving options where the premium paid qualifies for income tax rebates under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, and the maturity benefit may qualify for tax deductions under Section 10(10D) of the Income Tax Act.
2. What are some typical terms associated with Life Insurance Plans
- Term
The number of years that the policyholder will be covered under the policy. At the end of the term the policy matures and the individual will be entitled to receive maturity benefits and other accrued bonuses. - Grace Period
The grace period is an extension of time granted to the policyholder if he is unable to make a payment within the deadline. It is usually 15 to 30 days. - Free-look Period
A small amount of time provided after the inception of a new policy, allowing for the cancellation of the policy in case the policyholder is unsatisfied with the terms. - Lapsed Policy
When the policyholder doesn’t make payments within the deadline, nor even after the grace period, the insurance benefits stop and the policy is canceled. The canceled policy is known as a lapsed policy. - Sum Assured
The amount of lump sum guaranteed to the policyholder at the maturity of the policy in case the policyholder outlives the term of the policy. Additionally, there may be other payable benefits accrued along with the sum assured. - Death Benefit
The payout receivable by the beneficiary/nominee in case of premature death of the policyholder/insured during the subsistence of the term of the policy - Accidental Benefit
The bonus amount payable in addition to the death benefit, in case of premature death of the policyholder/assured during the subsistence of the term of the policy, but only in case of death is caused due to an accident. - Cash Value
The value payable to the policyholder if the policy is canceled prematurely before completion of the term. The cash value is the cost at which the policy can be sold at that moment. It keeps on increasing with the amount of premium paid. - Reinstatement
The policyholder can have an option to renew a lapsed policy after the grace period by making payment along with a penalty. This is called reinstatement of the policy. - Rider
Riders are extra features that whereby the policyholder becomes eligible to receive bonus payments and extra benefits on the occurrence of particular events. These enhance the value of the policy. - Vesting Age
Vesting age is when a policyholder starts receiving payouts from the policy. For child insurance policies vesting age is the age when the policy is transferred to the child who becomes the new policyholder. Usually, this happens when the child turns 18 years of age. - Waiver of Premium
One of the riders where the policyholder is absolved of the responsibility to make payments after suffering from a disability, but continues to receive stipulated benefits under the policy regardless.
3. What are the Types of Life Insurance Plans in India?
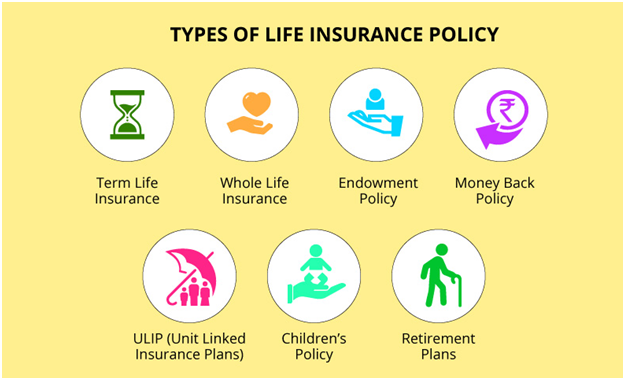
- TERM INSURANCE PLAN
Term insurance is one of the most basic types of life insurance policy where unlike permanent life insurance, there is an expiry date, within which if the policy-holder dies, then the beneficiaries get a death benefit which is an assured sum under the policy.- Types of Term Insurance available in India
Term Insurance is mainly classified into four broad categories –- a). Level Term Insurance
The premium rate remains fixed for the entire term of the plan. This is especially profitable to buy when you are young as Premiums payable would be low and you will not be charged a larger amount of premium as you become older. Also, the rate of premium doesn’t increase with the rate of inflation of the economy. - b). Increasing Term Insurance
The rate of premiums remains fixed even though the sum assured or death benefit increases periodically every year, up till a certain point or till an unlimited range, depending on the policy terms. It is also a great policy to counter the effects of inflation, but the premium is higher than Level Term Insurance. - c). Decreasing Term InsuranceThe premiums remain constant but the death benefit keeps on decreasing every year and tends to become zero towards the expiry of the term. Decreasing Term Insurance policies offer the lowest premiums among all types of plans and are usually purchased with a specific debt in mind.
- d). Term Insurance with Return of Premium (TROP)
Unlike vanilla term insurance, the amount of money paid as premium is returned to the policyholder at the expiry of the Term. It is understandable, however, that premiums are TROP plans are thus quite high compared to the rest of the term insurance plans.
- a). Level Term Insurance
- Types of Term Insurance available in India
- UNIT LINKED INSURANCE PLAN
Unit Linked Insurance Plans (ULIP) use part of your money to provide you with life insurance cover and the other part is invested in equity or debt instruments like shares or bonds. According to the changes brought in by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) in 2010, the ULIPs have now an increased lock-in period of 5 years, however considering that life insurance is an integral part, you should look at holding it for the entire term of the ULIP i.e. 10 to 15 years to reap the maximum benefit.- Types of ULIPs
On the basis of types of funds invested in, ULIPs may be classified as: - Equity funds
Here the majority of the investment is made in stocks and shares with a high risk but a potentially higher rate of return. - Debt funds
Here the majority invested in debt instruments with lower risk and a lower rate of return, and a Balanced fund with a balance between the two.
On the basis of the benefit conferred on the death of a policyholder, ULIPs may be classified as” - Type 1 ULIP
This pays the sum assured or the fund value to the nominee, whichever is high. - Type II ULIP
This pays both the sum assured and the fund value.
- Types of ULIPs
- ENDOWMENT PLAN
Endowment Plans are a combination of traditional term life insurance plan with a savings scheme, whereby the policy-holder is paid a sum assured or the maturity benefit if he outlives the expiry of the term of the policy. In case of premature death, the nominee will receive a sum assured plus a bonus amount which is the death benefit. Many plans also offer bonus payments throughout the term of the policy.- Types of Endowment Plans in India
- Endowment plans can be broadly classified into four major types –
- Unit Linked Endowment Plan
With Unit Linked Endowment Plans (ULEP), a share of the premium is kept as towards an assured sum and the rest is contribute to a common pool towards maturity benefit, which is invested into different types of funds in the market, type of which can be chosen by the policyholder during purchase of the plan, The common pool is then bifurcated into units and a number of units may be allocated to the policyholder depending on his contribution to the fund. This type of plan is thus obviously subject to market risk. - With- Profit Endowment Plan
Under With-Profit Endowment Plans, the policyholder is guaranteed a sum assured at maturity or as a death benefit in case of premature demise of the policyholder. However, along with it, the insurer may from time to time also provide period bonuses to the policyholder. The bonuses are not fixed, however, and the quantum depends on the amount of the investment made by the policy-holder and the profits of the insurer during that time. As such plans provide bonuses, they can generally be used to pay off mortgages. - Full Endowment Plan
Usually the benefit received at maturity may be less than the death benefit at the premature demise of a policyholder, however, in the case of Full Endowment Policy, the sum assured is guaranteed to be equal to the death benefit. Additionally, there is also some amount of bonus given at maturity. However, the premiums may be on the higher side. - Low-Cost Endowment Plan
Low-Cost Endowment Plans have a mixture of an element of decreasing term insurance and an element of investment. In decreasing term insurance, the death benefit and sum assured keeps on decreasing every year, and tend to become zero towards the expiry of the term. Thus, these plans are used rather to pay off a specific debt like mortgages, rather than as a true life insurance policy.
- Unit Linked Endowment Plan
- Endowment plans can be broadly classified into four major types –
- Types of Endowment Plans in India
- MONEY BACK INSURANCE PLAN
In money-back insurance plans where a percentage of the total sum assured is paid back to the policyholder at periodic intervals during the term. This is called a survival benefit. If the policyholder survives the total duration of the term, the remaining sum assured is paid along with some additional bonuses. However, what is unique about this type of insurance plan is that, if the policyholder dies prematurely during the term, the total sum assured calculated at the inception of the policy is paid regardless of the percentage of the sum assured already paid to the policyholder as survival benefit. - WHOLE LIFE INSURANCE PLANS
A whole life insurance policy as the name suggests is designed to cover the whole life of the policyholder. The term of the policy is usually about 100 years. At the death of the policyholder, the beneficiaries would be entitled to a death benefit. If the policyholder outlives the term of the policy then the sum assured and a bonus would be payable. The unique thing about a whole life policy is that premiums do not need to be paid for the whole term (in case of limited payment whole life insurance plans). Premiums payments would cease when the sum assured has been collected. So if a whole life policy is started when the policyholder is young with a modest sum assured, then the premium payments would cease very soon and the policy would last the entire lifetime of the policyholder. - Types of whole life plans available in India
- Non-participating Whole Life insurance Plan
This is the lowest costing whole life plan. It has a fixed premium and face value amount. There are no dividends or bonuses payable in this type of policy. - Participating Whole Life Insurance Plan
The premiums in this type of plan are slightly higher than the non-participating type. There is a fixed sum assured along with variable bonuses. The premiums are invested by the company and depending upon how those investments perform, the amount of bonus payable is decided on the profits generated from those investments. However, it must be understood that as those investments are subject to the market risk, there are no guaranteed bonuses payable every year. They may be a lump sum payment or in the form of a reduction of payable premiums to offset the cost of the policy. You can also use your bonus to increase the value of your sum assured thereby inflating the face value of the policy. - Level Premium Whole Life Insurance Plan
In this type of plan, the rate of premium remains constant and is payable throughout the life of the policyholder, as long as he remains alive. The final sum assured as death benefit varies on the corpus accumulated till death. - Limited Payment Whole Life Insurance Plan
In this type of plan, the premiums are higher than level premium plans, but only have to be paid for a fixed number of years, after which the policy still remains active till the death of the policyholder or till the maturity of the term of the policy which is usually 100 years. - Single-Premium Whole Life Insurance Plan
In this type of plan, there are no regular premium payments. Only a single lump sum payment is made at the inception of the policy which becomes fully funded throughout its life. This type of policy is very efficacious for use as an investment as the money is invested and rapidly builds up making for a large sum assured on the death of the policyholder. - Intermediate Premium Whole Life Insurance Plan
This type of plan has two different rates of premiums, one higher maximum guaranteed rate, and one lower rate. The lower premium is charged during the early years of the term and then the higher premium rate is decided after the performance of the investments made with the lower premium rate, to meet the maximum guaranteed rate.
- Non-participating Whole Life insurance Plan
- CHILD INSURANCE PLANS
Child Insurance Plans are specially designed to meet major expenses in the life of a child such as a college and a university, or marriage. In case the term of the policy expires the maturity benefit and sum assured paid to the child (who will become the policyholder as the policy becomes vested in him when he turns 18) ensures a corpus for the youth as he ventures into adulthood. This corpus can be used for various purposes such as investing in his first house, first car or first business venture. A good child insurance plan is one of the best gifts that you can bestow on your child.- Types of Child Insurance Plans
- Unit Linked Child Insurance Plans (ULIP)
These types of plans invest a part of the money in equity or debt instruments in the market and the other part is used to provide a fixed sum assured. This type of plan is especially good for longer tenures of more than 10 years and thus the maximum benefit is achieved when invested during the infantile years of the child. Also, the policy will typically offer flexibility to switch between equity and debt instruments according to your preference so that you can guard yourself against market risk. - Traditional Endowment Plans
These types of plans provide regular periodic bonuses over the term of the policy, usually from the second year onwards, in addition to a sum assured at maturity. Thus, this type of policy is very useful to secure expenses such as school and other needs of the child until adulthood as there are periodic bonus payments.
- Unit Linked Child Insurance Plans (ULIP)
- Types of Child Insurance Plans
- What is Vesting Age in Child Insurance Plans?
When child insurance plans are purchased, the policyholder is the one who pays the premiums, i.e. the parent. The vesting age feature usually presents in all child insurance plans transfers the policy to the child wherein the child becomes the policyholder. The vesting age is usually when the child attains adulthood at 18 years. - PENSION PLANS
Pension plans, also called retirement plans are specifically designed to provide an income to the policyholder, whether periodic payments or a one-time lump sum amount, at the retirement of the policyholder when he turns 60 years of age. The stage before retirement is called the accumulation stage when premiums are paid, and the stage after retirement is known as the distribution stage when the benefits are paid.- Types of Pension Plans in India
- Deferred Annuity Plan
In this type of plan, a lump-sum payment or regular premiums are paid during the accumulation stage, and period benefits in the form of pension would start after retirement during the distribution stage. This type of pension plan is totally exempt from taxes unless money is withdrawn during the accumulation state. - Immediate Annuity Plan
In this type of plan, the pension payments start immediately during the accumulation period according to the number of contributions made by premiums. The premium paid is exempt from tax but not the benefits. Immediate annuity plans can be further divided into Guaranteed Period annuity plans where the annuity benefits are paid only for a certain period of time, and Life Annuity plans where the annuity benefits continue till the entire lifetime of the policyholder. - With or without cover Pension Plan
In case of cover plans, in case of the death of the policyholder during the term, the nominee/beneficiary will get a sum assured which is higher than the accumulated corpus of the premiums paid. In case of without cover, the nominee/beneficiary would only get an amount equal to the corpus of the premiums paid. - National Pension Scheme (NPS)
This scheme is introduced by Govt. of India where the policyholder pays periodic payments which are used to invest in equity and debt instruments in the market. Upon retirement, the policyholder’s corpus grown by the method.
- Deferred Annuity Plan
- Types of Pension Plans in India
4. What are the common exclusions in Insurance policies in India?
Insurance plans may cover a whole list of benefits, however, there are some instances when the death benefit might be rejected to be paid by the insurance companies. These circumstances are known as exclusions. Here are some common exclusions in policies.
- Death due to Suicide
Suicide is one of the most common exclusions in all insurance policies, and this exclusion often applies in case of group insurance policies also. However, depending upon the specific policy terms, all premiums paid till the expiry of the policyholder may be returned without interest and subject to deduction of penalties and administrative expenses. - Death as a direct result of the actions of the policy-holder
If the death can be proved to have been directly caused by the policyholder and occurred under unnatural circumstances, such as rash driving or driving under the influence, extreme sports, engaging in otherwise risky circumstances, etc., the benefit payable on the demise of policyholder may be refused. - Death due to intoxicants or narcotics
Another common exclusion is the death of the policyholder due to the consumption of alcohol or narcotics leading to overdose or related circumstances causing death such as drunk driving. - Death due to war or terrorism or natural calamities
Some policies also exclude benefits in case of death due to collateral damage as a result of war, terrorism or any natural calamity such as drought, etc. - Death due to self-inflicted injury
If the policyholder engages in a risky activity without the proper precautions, the direct result of which causes the death of a person, the benefit would be excluded. Some examples are hazardous to work like construction without safety gear and extreme sports. - Death due to sexually transmitted diseases
A lot of policies also exclude death due to sexually transmitted diseases or infections like HIV, AIDs, chlamydia, etc.
5. What are Riders and how can they enhance Insurance Policies?
A traditional Insurance plan only covers benefits on the death of the policyholder along with some bonus payments. However, riders can be included in the policy to cover other types of benefits as well. Here are some of the various riders providing different types of coverage.
- Permanent & Partial Disability
This rider activates in case the policyholder, unfortunately, meets with an accident and is left with a permanent or partial disability, forcing circumstances where the policyholder may be unable to work. In that case, the insurance provider would pay a lump sum or regular payments for the next 5-10 years depending upon the policy term to help the policyholder cope with expenses and the loss of income. Often times, this is combined with accidental death riders. - Critical Illness
This rider provides a lump sum payment when the policyholder gets get afflicted with a major illness or medical condition such as heart or kidney failure, brain stroke, etc. requiring major surgeries. It is very important to check the policy document carefully as often times in case of activation of this rider, the ultimate death benefit may be reduced. - Accidental Death
This rider provides twice the amount of sum assured death benefit, in case the policyholder passes away due to an unfortunate accident in case of natural causes. Also called double indemnity rider. It is important to remember than in case the policyholder dies for reasons other than an accident, this rider will not get activated, and the death benefit will be the normal assured amount. - Waiver of Premium
This rider gets activated if the policyholder gets afflicted with a critical illness or serious medical condition leaving him unable to pay the premium of the policy. In that case, all future premiums are waived off but the policy continues to remain active. It is important to note that generally, insurance policies impose a long wait time before the activation of this rider. - Income Benefit
The income benefit rider kicks in when the policyholder was the sole provider of the family at the time of his death. In that case it provides the family with regular periodic payments as a source of income, usually, a percentage of the sum assured.
6. Is it a good idea to buy two or more Life Insurance Plans?
There is no wrong or right answer to this question. Sometimes it is better to diversify your portfolio and invest in different types of plans to meet different goals. For others, it is better to stick to one policy. Let us look at some advantages and disadvantages of splitting cover between multiple policies.
- Advantages
- Splitting can give your flexibility of bifurcating your cover in different ratios in between plans depending upon factors like variable benefits, exposure to market risk, the quantum of sum assured, bonuses, riders, etc.
- Life insurance policies are most important for times when they are many people dependant on you such as when your kids are younger. After they get older and find employment on their own, the pressure on your becomes lighter and you may have the freedom to cancel one or more policies you don’t need and enjoy the lump sum benefit.
- Splitting allows you to enjoy more benefits from newly introduced plans in the market, as newer plans tend to have more favorable terms because of increased competition in the insurance business.
- Splitting allows you to choose plans with different maturity dates and enjoy maturity benefits throughout your life or plan for crucial moments, like children’s higher education, buying a house, car, or an expensive vacation.
- Splitting allows you to have variable assured sums for different beneficiaries depending on how dependent they may be.
- Disadvantages
- Multiple policies mean that you would be burdened with more documentation and hassles of managing them.
- You would have to undergo multiple medical examinations each time for a new policy.
- You would have to file multiple claims each requiring separate documentation.
- Your premium expenses might become quite high and thus meticulous financial planning is required for managing multiple policies.
- Splitting of premiums means that you might miss out on special discount thresholds that you might have met had you invested the whole amount in one policy.
7. How to get Tax Benefits on Life Insurance Policies
- Deduction for Premium under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act
If the policy has been issued after April 2012 and availed with parents, spouse or children as beneficiary, and the premiums paid are within 10% of the sum assured, then such premiums would be tax-deductible under Section 80C. - Exemption for Maturity Benefit under Section 10(10D) of the Income Tax Act
The maturity amount received at the end of the policy term will be completely tax exempt in case of a policy issued after April 2012, and the premium paid on the policy does not exceed 10% of the sum assured.
8. What are the factors which affect how much premium is chargeable
There may be a number of factors considered by the life insurance company to decide on the premium payable. They are as follows –
- Age
The most important factor in a life insurance policy is age. The younger you are when the policy is purchased, the less the premium that will be charged. This because it is generally perceived that older people are at a greater risk of contracting major illnesses and thus older people are riskier for life insurance companies. - Health Records and Medical History
Health records are thoroughly inspected by insurance companies before inducting someone into a new policy. Thus a person with a clean health record is liable to be charged less premium than a person with major illnesses in their past, as they are generally believed to have a weaker immune system. - Gender
Though gender is not that big of a factor, females have on average statistically shown to live longer by about 5 years more than males. Females are generally charged a bit lower premium than males. - Smoking and Drinking
Smoking and drinking, especially smoking is a big factor and a cause for multiple illness like lung, heart, liver and kidney problems in later life. Thus, smokers and the habitual drinkers will be charged a considerable high premium than a non-smoker and teetotaler. - Profession
Individuals with professions having a higher than normal risk of dying or contracting an illness will be liable to be charged higher premiums. For e.g., a race car driver or a policeman will be charged more than say a teacher. - Lifestyle and Hobbies
Individuals have riskier hobbies which may put them in harm’s way such as mountain climbing, extreme sports like snowboarding, car racing will be charged higher premiums. - Obesity
Obesity is associated with many conditions and illnesses like heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, osteoporosis, etc. making them riskier candidates for life insurance companies. Thus they will be charged higher premiums. Many policies also offer an incentive by lower premiums things like gym membership, lowering BMI, doctor checkups, etc.
9. How to decide how much life insurance is needed
The amount of life insurance that is needed by someone can be decided by keeping in mind some of the following factors.
- Expenses and liabilities
You should keep in mind your current day to day expenses such as utility bills, loan payments, children’s school tuition fees, groceries, etc. Big future expenses like college for children, their marriage, your retirement planning, etc. should also be kept in mind. Now, this is to be considered with your current and prospective income on the other hand to get a rough estimate. - Income Multiplier Procedure.
A simple procedure to estimate the term of insurance and required sum assured considering age and income is to multiply your current income by a factor. If you are between 20 to 30 years, then multiply incomes by 25, if 30 to 40 then multiply by 15, if between 40 to 50 then multiply by 10 and for 50 to 60 multiplied by 5. Please note this is a rough generalized estimate and your particular needs may vary. - Online Human Life Value Calculator
Automatic Human Life Value Calculators are available online to calculate the sum assured, which takes into consideration certain factors like estimated future income, current and future expenses, etc, relieving you of the burden of calculation and minimizing human error. These calculators have been developed by experts after years of experience and study of statistical means.
10. How to File a Life Insurance Claim in case of death of the Insured
In case of the death of the insured, the nominee/beneficiary family members or assignees (if the policy has been assigned) have to file a claim with the insurance provider in the following manner –
- The insurance provider should be informed as soon as possible after the confirmation of the death of the insurer.
- The Death Certificate has to be submitted along with the claim form.
- The Discharge form should bear the signature of witnesses.
- The original policy document is legal proof of the validity of the policy.
- The legal proof of identity and the title of the claimant has to be submitted.
- If post-mortem has been conducted, such reports need to be submitted.
- If the matter is such that police inquiries have been conducted, inquest reports on such enquiries have to be submitted.
- An employer’s certificate also may be needed to be submitted.
11. How to File a complaint against an Insurance Provider?
If you are unsatisfied or feel like the claim has been unfairly rejected, or deliberately delayed, then there are a few avenues to explore for redressal.
- A grievance may be lodged with the designated grievance redressal officer of the insurance provider itself, who is usually a member of the senior management.
- A formal complaint may be lodged with the insurance ombudsman of the Executive Council of Insurers of the concerned state whose decision is binding on the insurance provider.
- A complaint may be lodged with the grievance redressal cell of the consumer affairs department of the Insurance Regulatory Authority of India (IRDA) by sending an email at complaints@irda.gov.in or by a phone call on 155255 (or) 1800 4254 732. The IRDA may also be contacted through the Integrated Grievance Management System (IGMS) at igms.irda.gov.in.
- Finally, you can also complain to the National Consumer Helpline by signing up online, giving a call on 1800-11-4000 or 14404 or SMS to 8130009809 or signing up on the app, litigation may be lodged at a consumer court of the judiciary. Off late there has been an increase in private complaints against insurance companies.